KyotoTech Logger
Introduction
KyotoTech Logger is a cloud logging platform for .NET applications. It consists of:
- NuGet SDK — A lightweight .NET library that you integrate into your application
- Web Dashboard — A browser-based interface for viewing, searching, and managing logs
- REST API — HTTP endpoints for log ingestion and management
Key Features
- One-liner initialization
- 150+ log categories (ErrorLog, SecurityLog, DatabaseLog, etc.)
- Automatic remote upload with offline fallback
- Custom metadata on every log entry
- Zero external dependencies (everything embedded in one DLL)
- Cross-platform: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android
- Supports Console, ASP.NET Core, MAUI, WPF, WinForms, Blazor
System Requirements
| Requirement | Minimum |
|---|---|
| .NET Version | .NET 8.0 or higher |
| OS | Windows 10+, macOS 12+, Linux (x64/arm64), iOS 16+, Android 10+ |
Getting Started
Step 1: Create an Account
- Go to logger.kyototech.co.jp and register
- You will receive an Organization with a Free plan
Step 2: Create a Project
- Log in to the Dashboard
- Go to Projects and click Create Project
- Enter a project name, choose a color and platform type
Step 3: Create an API Key
- Open your project settings
- Under API Keys, click Generate New Key
- Choose a name and environment (production, staging, development)
- Copy the key immediately — it is only shown once
- API Key format:
ktlog_production_a1b2c3d4...
Step 4: Install the NuGet Package
dotnet add package KyotoTechLoggerOr via Package Manager Console:
Install-Package KyotoTechLoggerOr in your .csproj:
<PackageReference Include="KyotoTechLogger" Version="1.2.2" />Step 5: Initialize and Log
using KyotoTechLogger;
using KyotoTechLogger.Models;
using System.Reflection;
// Initialize (once at app startup)
var result = LogService.Initialize(
licenseKey: "YOUR-LICENSE-KEY",
apiKey: "ktlog_production_your_key_here",
serverUrl: "https://logger.kyototech.co.jp/api/v1/logs");
if (!result.Success)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Init failed: {result.ErrorMessage}");
return;
}
// Log a message
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
"Application started",
LogTypes.LifecycleLog);
// Upload logs to the dashboard
await LogService.Instance.UploadLogsAsync();License Key vs. API Key
License Key = Delivered with your subscription (format: TIER-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX)
API Key = Created by you on the dashboard under Project Settings
NuGet SDK Reference
Initialization
All initialization requires three parameters: licenseKey, apiKey, serverUrl.
// Synchronous (Console, WPF, WinForms)
var result = LogService.Initialize(licenseKey, apiKey, serverUrl);
var result = LogService.Initialize(licenseKey, apiKey, serverUrl, options => { ... });
// Asynchronous (ASP.NET Core, MAUI)
var result = await LogService.InitializeAsync(licenseKey, apiKey, serverUrl);
// From license file (offline activation)
var result = LogService.InitializeWithFile(licensePath, apiKey, serverUrl);
var result = await LogService.InitializeWithFileAsync(licensePath, apiKey, serverUrl);The InitializationResult tells you whether it succeeded:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Success | bool | Whether initialization succeeded |
Message | string? | Status message |
ErrorMessage | string? | Error details if failed |
LicenseInfo | LicenseInfo? | License details |
Configuration Options
Pass an options callback to configure behavior:
var result = LogService.Initialize(licenseKey, apiKey, serverUrl, opts =>
{
opts.ShowConsole = true; // Print logs to console
opts.ShowConsoleDebug = true; // Print to debug output
opts.TimeoutSeconds = 15; // HTTP timeout for uploads
opts.MaxLogAgeDays = 30; // Local log retention
opts.RemoteLogTypes = new List<LogTypes> // Only upload these types
{
LogTypes.ErrorLog,
LogTypes.CrashLog,
LogTypes.SecurityLog
};
});| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ShowConsole | bool | false | Print logs to console output |
ShowConsoleDebug | bool | false | Print to debug output |
TimeoutSeconds | int | 30 | HTTP timeout in seconds |
MaxLogAgeDays | int | 30 | Local file retention in days |
RemoteLogTypes | List<LogTypes>? | null (all) | Which log types to upload. null = all |
Logging Methods
After initialization, use LogService.Instance to log:
// Log a message
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
"User logged in successfully",
LogTypes.AuthLog);
// Log an exception
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
ex,
LogTypes.ErrorLog);
// Log with custom metadata (v1.2.0+)
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
"Order processed",
LogTypes.BusinessLog,
new Dictionary<string, object>
{
["orderId"] = "ORD-12345",
["amount"] = 99.99,
["currency"] = "USD",
["items"] = new[] { "SKU-001", "SKU-002" }
});
// Log an exception with metadata
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
ex,
LogTypes.ErrorLog,
new Dictionary<string, object>
{
["userId"] = currentUserId,
["endpoint"] = "/api/orders"
});Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
method | MethodBase? | Use MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod() for automatic caller info |
message | string | The log message |
exception | Exception | The exception object (message + stack trace captured) |
logType | LogTypes | Category of the log entry |
metadata | Dictionary<string, object>? | Optional custom key-value data |
Uploading Logs
Logs are stored locally and uploaded on demand:
// Upload all pending logs
var uploadResult = await LogService.Instance.UploadLogsAsync();
// Upload specific log types only
await LogService.Instance.UploadLogsAsync(new List<LogTypes>
{
LogTypes.ErrorLog,
LogTypes.CrashLog
});
// Upload previously failed logs (backup files)
await LogService.Instance.UploadBackupFilesAsync();
// Clean up old local log files
await LogService.Instance.RemoveAllOldLogFilesAsync();The UploadResult provides details:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
IsSuccess | bool | Whether the upload succeeded |
Message | string? | Status message |
ErrorMessage | string? | Error details if failed |
TotalLogsUploaded | int | Number of logs sent |
Runtime Configuration
You can change settings after initialization:
LogService.Instance.SetApiKey("ktlog_production_new_key");
LogService.Instance.ToggleShowConsole(true);
LogService.Instance.SetRemoteLogTypesAllowToSend(new List<LogTypes> { LogTypes.ErrorLog });
LogService.Instance.SetMaxLogsAge(14);
LogService.Instance.SetDefaultServerUrl("https://logger.kyototech.co.jp/api/v1/logs", 30);License Information
var info = LogService.Instance.GetLicenseInfo();
Console.WriteLine($"Type: {info.LicenseType}");
Console.WriteLine($"Valid: {info.IsValid}");
Console.WriteLine($"Expires: {info.ExpirationDate?.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd") ?? "Never"}");
Console.WriteLine($"Max Logs/Day: {info.MaxLogsPerDay}");Log Types
There are 150+ log types. Here are the most commonly used:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ErrorLog | Application errors |
CrashLog | Crash reports |
WarningLog | Warning messages |
DeveloperLog | Developer/debug info |
SecurityLog | Security events |
AuthLog | Authentication events |
PerformanceLog | Performance metrics |
DatabaseLog | Database operations |
NetworkMonitorLog | Network activity |
RestLog | REST API calls |
HttpLog | HTTP activity |
CacheLog | Cache operations |
UILog | User interface events |
LifecycleLog | App lifecycle (start, stop) |
FileLog | File operations |
ConfigLog | Configuration changes |
AuditLog | Audit trail |
HealthCheckLog | Health check results |
BusinessLog | Business logic events |
NotificationLog | Notification events |
Tip
Use IntelliSense in your IDE to explore all available LogTypes.
Code Examples
Console Application
using System.Reflection;
using KyotoTechLogger;
using KyotoTechLogger.Models;
var result = LogService.Initialize(
licenseKey: "STR-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX",
apiKey: "ktlog_production_your_key",
serverUrl: "https://logger.kyototech.co.jp/api/v1/logs",
options: opts => opts.ShowConsole = true);
if (!result.Success)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Failed: {result.ErrorMessage}");
return;
}
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
"Application started",
LogTypes.LifecycleLog);
try
{
// Your code here
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
ex,
LogTypes.ErrorLog);
}
await LogService.Instance.UploadLogsAsync();ASP.NET Core
// Program.cs
using KyotoTechLogger;
using KyotoTechLogger.Models;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var logResult = await LogService.InitializeAsync(
licenseKey: "ENT-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX",
apiKey: "ktlog_production_your_key",
serverUrl: "https://logger.kyototech.co.jp/api/v1/logs",
options: opts =>
{
opts.TimeoutSeconds = 15;
opts.RemoteLogTypes = new List<LogTypes>
{
LogTypes.ErrorLog,
LogTypes.SecurityLog,
LogTypes.AuthLog,
LogTypes.PerformanceLog
};
});
var app = builder.Build();
app.Run();.NET MAUI
// MauiProgram.cs
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder.UseMauiApp<App>();
var result = LogService.Initialize(
licenseKey: "DEV-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX",
apiKey: "ktlog_production_your_key",
serverUrl: "https://logger.kyototech.co.jp/api/v1/logs",
options: opts =>
{
#if DEBUG
opts.ShowConsole = true;
#endif
opts.MaxLogAgeDays = 14;
opts.RemoteLogTypes = new List<LogTypes>
{
LogTypes.ErrorLog,
LogTypes.CrashLog
};
});
return builder.Build();
}
}Background Upload Service
For applications that run continuously, set up periodic uploads:
public class LogUploadService : BackgroundService
{
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested)
{
await LogService.Instance.UploadLogsAsync();
await LogService.Instance.UploadBackupFilesAsync();
await LogService.Instance.RemoveAllOldLogFilesAsync();
await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5), stoppingToken);
}
}
}Using Custom Metadata
Attach structured data to any log entry:
// E-commerce example
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
"Payment processed",
LogTypes.BusinessLog,
new Dictionary<string, object>
{
["orderId"] = "ORD-2026-0001",
["amount"] = 149.99,
["currency"] = "USD",
["paymentMethod"] = "credit_card",
["customerId"] = "CUST-789"
});
// Error with context
catch (Exception ex)
{
LogService.Instance.Log(
MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod(),
ex,
LogTypes.ErrorLog,
new Dictionary<string, object>
{
["userId"] = currentUser.Id,
["requestPath"] = context.Request.Path,
["requestMethod"] = context.Request.Method
});
}Metadata supports primitives, strings, arrays, and nested objects. It is displayed as structured data in the Dashboard.
Web Dashboard
The Dashboard is available at logger.kyototech.co.jp.
Dashboard Overview
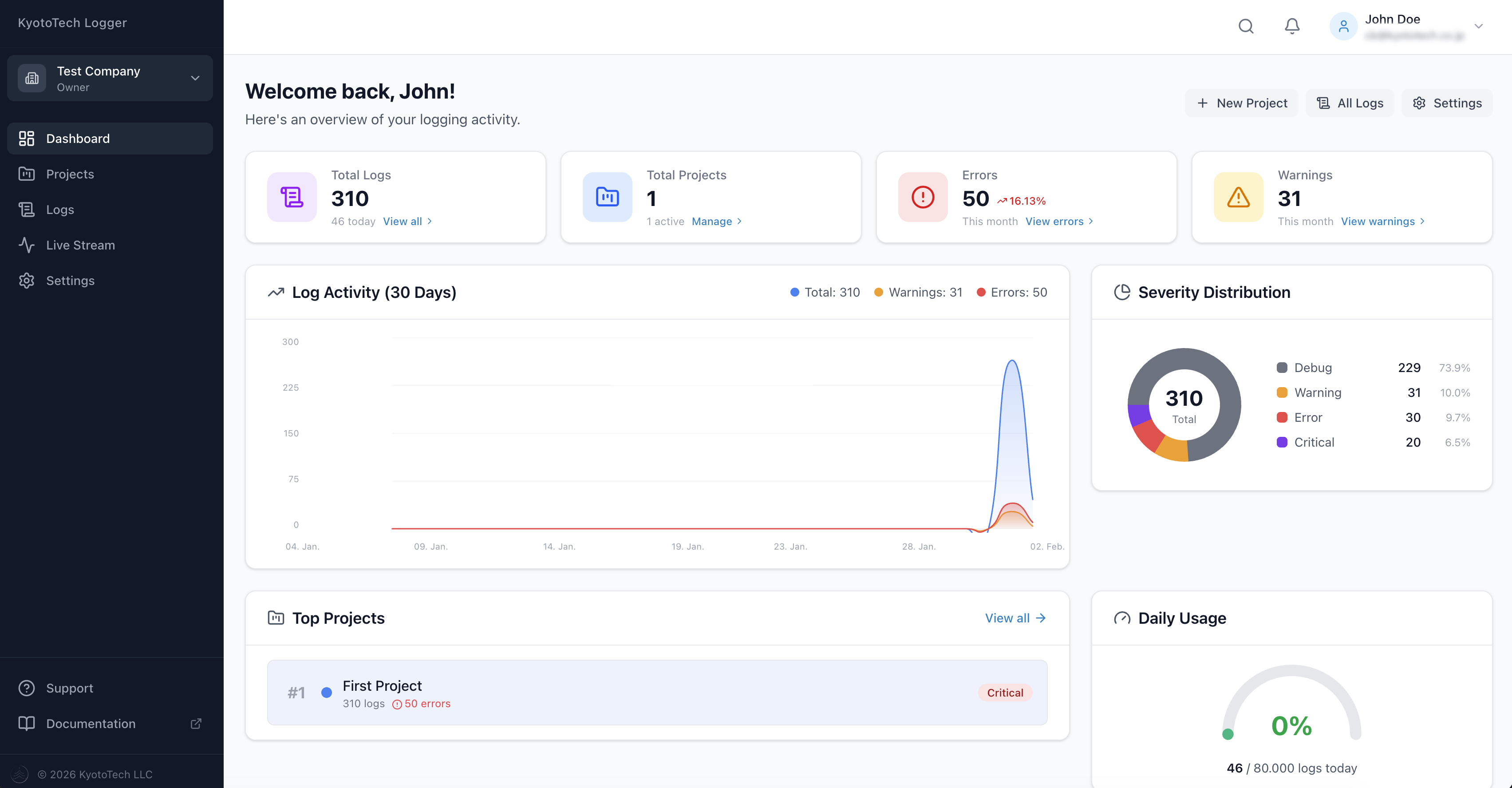
The main dashboard shows:
- Log statistics — Total logs, today's count, errors, warnings
- Usage gauge — Daily log usage vs. your plan limit
- Trend chart — Log volume over time (7–90 days)
- Severity distribution — Breakdown by Debug, Info, Warning, Error, Critical
- Top projects — Your most active projects
- Recent errors — Latest error and critical logs
Log Viewer
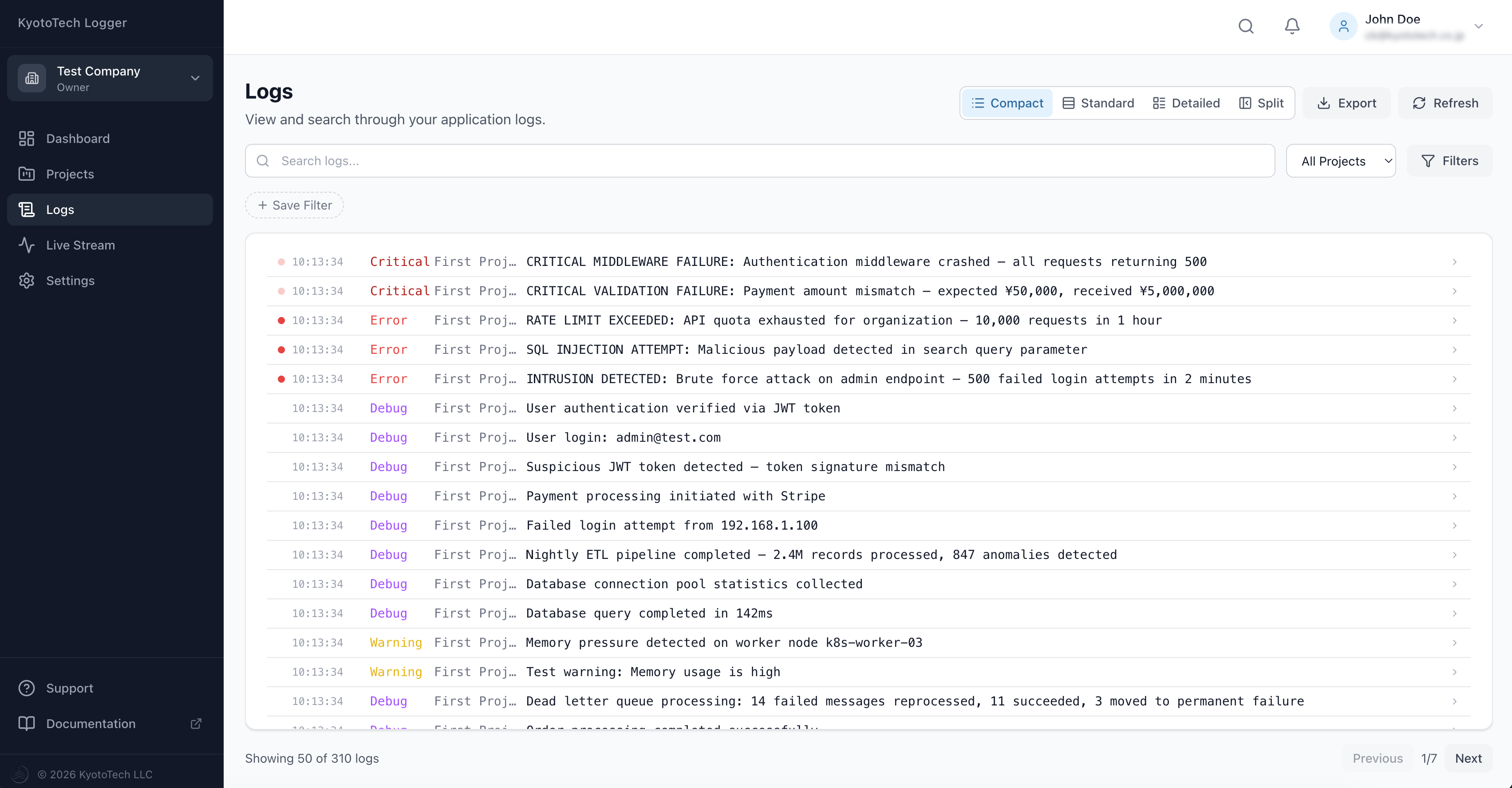
The log viewer provides four display modes:
- Compact — One-line overview, ideal for scanning large volumes
- Standard — Balanced view with key information (default)
- Detailed — Full log entry with all fields expanded
- Split View — List on the left, details panel on the right
Searching & Filtering
- Free-text search — Search in messages, methods, exceptions, and timestamps
- Severity filter — Filter by Debug, Info, Warning, Error, Critical
- Project filter — Show logs from a specific project
- Date range — Filter by time period
- Saved filters — Create and save filter combinations for quick access
Log Details
Click any log entry to see:
- Full message text
- Method name
- Exception details and stack trace
- Device information (OS, machine name, app version)
- Custom metadata (displayed as structured key-value pairs)
- Timestamps (client-reported and server-received)
- Comments (team members can add notes)
Projects
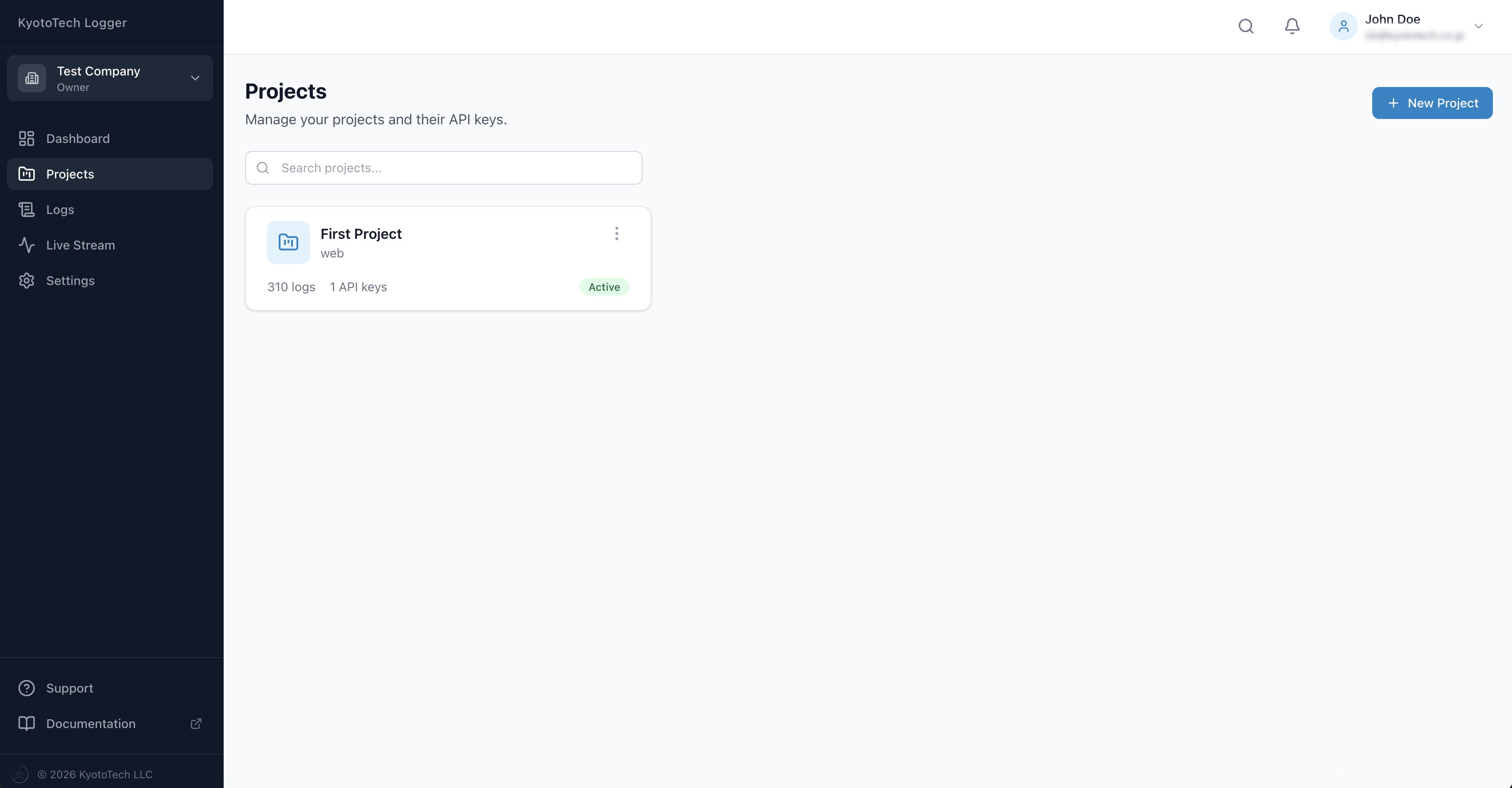
Each project has:
- A unique name, color, and icon
- One or more API Keys
- Statistics (total logs, logs today, error count)
- Platform tag (web, mobile, desktop, server)
API Key Management
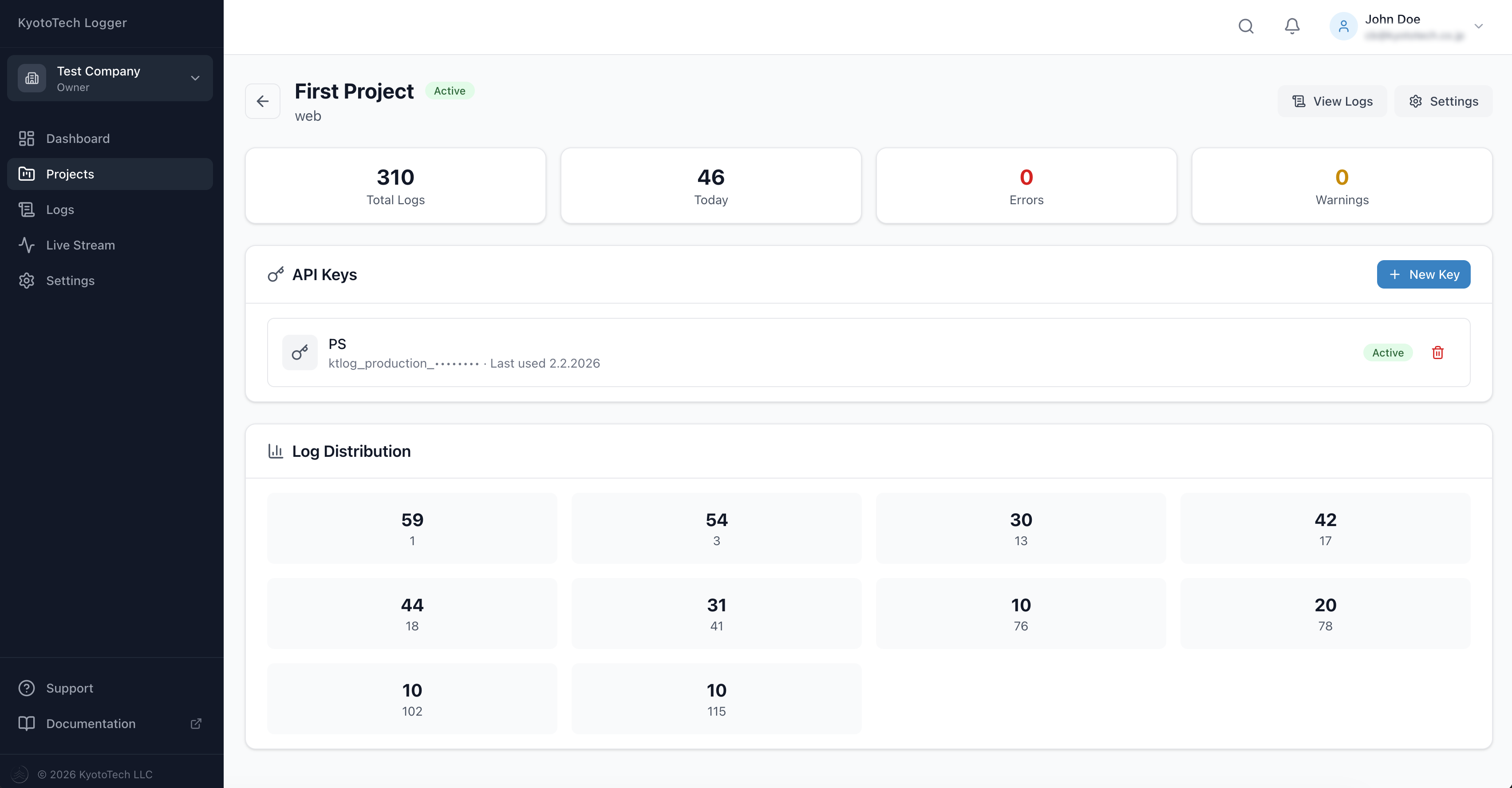
Under each project you can:
- Generate new API Keys (with environment: production, staging, development)
- Set optional expiration dates
- View usage statistics per key
- Revoke keys that are no longer needed
Note
API Keys are shown in full only at creation. After that, only the prefix and last 4 characters are visible.
Export
Export your logs in multiple formats:
- JSON
- CSV
Live Stream
Professional & Enterprise
The Live Stream feature is available on Professional and Enterprise plans.
The Live Stream page shows log entries in real time as your applications send them. It uses a WebSocket connection, so entries appear instantly without refreshing.
Accessing the Stream
Navigate to Live Stream in the sidebar. The page opens with a live connection to the server.
Stream Interface
- Live indicator — A pulsing dot in the header shows the connection status (red = streaming, amber = paused, gray = disconnected)
- Connection badge — Shows whether the WebSocket is connected
- Entry counter — Displays how many entries are currently visible
Filtering
All filtering happens client-side for instant response:
- Project filter — Dropdown to show logs from a single project
- Severity chips — Toggle Debug, Info, Warning, Error, and Critical on or off
- Search — Filter by method name or message text
Stream Controls
| Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Pause / Resume | Pauses the stream. Incoming entries are buffered and flushed when you resume. |
| Clear | Removes all entries from the display and resets the error counter. |
| Export | Downloads the currently displayed entries as a TSV file. |
Log Details
Click any entry row to expand it. The detail panel loads the full log from the server, including:
- Complete message text
- Custom metadata (as key-value tags)
- Exception details and stack trace (for error/critical entries)
- Quick actions: View Full Log (opens in the Log Viewer) and Copy JSON
Limits
- The stream keeps up to 500 entries in the browser. Older entries are automatically removed as new ones arrive (FIFO).
- Log messages in the stream are truncated to 200 characters. Click an entry to see the full text.
REST API Reference
If you do not use the NuGet SDK (e.g., you use a different programming language), you can call the API directly.
Base URL: https://logger.kyototech.co.jp/api/v1
Authentication
For log submission, include your API Key in the header:
X-Api-Key: ktlog_production_your_key_hereSubmit a Single Log
POST /api/v1/logsHeaders:
Content-Type: application/json
X-Api-Key: ktlog_production_your_key_hereBody:
{
"logType": 1,
"logTypeDescription": "ErrorLog",
"clientTimestamp": "2026-01-27T10:30:00Z",
"message": "Database connection timeout",
"methodName": "MyApp.Services.DbService.Connect",
"exception": "System.TimeoutException: Connection timed out",
"stackTrace": "at MyApp.Services.DbService.Connect() in ...",
"metadata": {
"server": "db-primary",
"retryCount": 3
},
"deviceInfo": {
"platform": "Linux",
"osVersion": "Ubuntu 22.04",
"machineName": "web-server-01",
"appVersion": "2.1.0"
}
}Response (201):
{
"success": true,
"logId": "a1b2c3d4-...",
"remainingLogsToday": 2847
}Submit a Batch of Logs
POST /api/v1/logs/batchBody:
{
"batchId": "batch-2026-01-27-001",
"deviceInfo": {
"platform": "Windows",
"appVersion": "3.0.0"
},
"logs": [
{
"logType": 1,
"logTypeDescription": "ErrorLog",
"clientTimestamp": "2026-01-27T10:30:00Z",
"message": "Error processing order"
},
{
"logType": 5,
"logTypeDescription": "WarningLog",
"clientTimestamp": "2026-01-27T10:30:01Z",
"message": "Slow query detected"
}
]
}Response (201):
{
"success": true,
"logsReceived": 2,
"logsStored": 2,
"batchId": "batch-2026-01-27-001",
"logIds": ["a1b2c3d4-...", "e5f6g7h8-..."],
"remainingLogsToday": 2845
}Log Field Reference
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
logType | int | Yes | Numeric log type ID |
logTypeDescription | string | Yes | Human-readable type name (max 64 chars) |
clientTimestamp | datetime | Yes | When the log occurred (ISO 8601) |
message | string | Yes | Log message content (max 65,536 chars) |
methodName | string | No | Method/function name (max 256 chars) |
exception | string | No | Exception message |
stackTrace | string | No | Exception stack trace |
innerException | string | No | Inner exception details |
metadata | object | No | Custom key-value pairs |
deviceInfo | object | No | Device/environment info |
batchId | string | No | Identifier for grouping (max 64 chars) |
HTTP Status Codes
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 201 | Log(s) successfully stored |
| 400 | Invalid request body or missing required fields |
| 401 | Invalid or missing API Key |
| 429 | Daily log limit reached |
| 500 | Server error |
Best Practices
Initialization
- Call
Initialize()once at application startup, before any logging - Store your API Key securely (environment variables, user secrets, Azure Key Vault, etc.)
- Never commit API Keys or License Keys to source control
- Use
InitializeAsync()in async contexts (ASP.NET Core, MAUI)
Choosing Log Types
- Only enable remote upload for log types you need (
RemoteLogTypesoption) - At minimum, use
ErrorLogandCrashLogfor production monitoring - Add
PerformanceLogfor performance-sensitive applications - Use
SecurityLogandAuthLogfor applications handling sensitive data
Uploading
- Logs are stored locally first and uploaded when you call
UploadLogsAsync() - Set up a periodic upload (e.g., every 5 minutes) using a background service or timer
- Call
UploadBackupFilesAsync()to retry previously failed uploads - Call
RemoveAllOldLogFilesAsync()periodically to clean up old local files
Metadata
- Use metadata for structured context (user IDs, request paths, order numbers, etc.)
- Keep metadata values concise — avoid large objects or binary data
- Use consistent key names across your application for easier searching
Security
- Use separate API Keys for production and staging environments
- Set expiration dates on API Keys and rotate them periodically
- Use HTTPS only (the server URL must start with
https://) - Do not log sensitive data (passwords, credit card numbers, personal IDs) in messages or metadata
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
Initialize() returns Success = false | Check that licenseKey, apiKey, and serverUrl are all provided and correct |
| Upload fails with 401 | Your API Key is invalid, expired, or revoked. Generate a new one on the dashboard |
| Upload fails with 429 | You have reached your daily log limit. Upgrade your plan or wait until the next day (resets at UTC midnight) |
| Upload fails with timeout | Increase TimeoutSeconds in options or check your network connectivity |
| No logs on dashboard | Ensure RemoteLogTypes includes the log types you are using. If set to null, all types are uploaded |
| License validation failed | Your License Key may not match your active subscription. Check your subscription status |
Checking Your Setup
// Check initialization
var result = LogService.Initialize(licenseKey, apiKey, serverUrl);
Console.WriteLine($"Success: {result.Success}");
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {result.ErrorMessage}");
// Check license
var info = LogService.Instance.GetLicenseInfo();
Console.WriteLine($"License Type: {info.LicenseType}");
Console.WriteLine($"Valid: {info.IsValid}");
Console.WriteLine($"Max Logs/Day: {info.MaxLogsPerDay}");
// Check hardware ID (for hardware-bound licenses)
Console.WriteLine($"Hardware ID: {LogService.Instance.GetHardwareId()}");
// Test upload
var upload = await LogService.Instance.UploadLogsAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Upload: {upload.IsSuccess} - {upload.Message}");Support & Contact
Resources
- Dashboard: logger.kyototech.co.jp
- NuGet Package: nuget.org/packages/KyotoTechLogger
- Pricing: kyototech.jp/pricing
- Support Contact: kyototech.jp/#contact
Reporting Issues
When contacting support, please include:
- Your License Key (first 8 characters only)
- Your application type (.NET MAUI, ASP.NET Core, Console, etc.)
- The
InitializationResultoutput or error message - Your Hardware ID if relevant:
LogService.Instance.GetHardwareId()
Legal Disclaimer
KyotoTech Logger is provided "AS IS" without warranty. KyotoTech LLC is not liable for data loss, service interruptions, or damages arising from use of this service. You are responsible for your API Keys and log data management. For full terms, see Terms of Service.
Copyright 2024-2026 KyotoTech LLC. All Rights Reserved.
This documentation is for KyotoTech Logger version 1.2.2.